e seek to improve efficiency of the finite difference scheme by splitting the
spacial operator
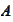 into some positive components
into some positive components
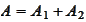 and replacing the inversion of
and replacing the inversion of
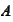 with consecutive inversions of
with consecutive inversions of
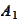 and
and
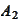 .
In this section we always assume that some original scheme already has
stability and approximation properties and we show how to separate operator
while keeping these properties.
.
In this section we always assume that some original scheme already has
stability and approximation properties and we show how to separate operator
while keeping these properties.
|