e price at time
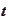 a contract to exchange
a contract to exchange
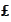 for
for
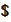 at a future time
at a future time
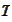 and for fixed exchange rate
and for fixed exchange rate
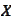 .
We determine a fair forward exchange rate
.
We determine a fair forward exchange rate
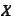 by the following argument. We purchase
by the following argument. We purchase
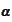 units of riskless
units of riskless
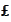 -bond,
short one riskless
-bond,
short one riskless
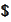 -bond
with maturity at
-bond
with maturity at
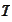 and enter into the exchange contract in question. The forward exchange rate
and enter into the exchange contract in question. The forward exchange rate
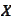 that makes such position of zero value is the correct exchange rate. These are
the
that makes such position of zero value is the correct exchange rate. These are
the
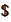 -values
of the replicating
position:
-values
of the replicating
position:
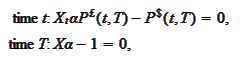 where we used
where we used
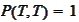 by definition of the bond and offset the contract in question at time
by definition of the bond and offset the contract in question at time
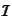 .
We obtained two equations for two unknown variables
.
We obtained two equations for two unknown variables
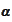 and
and
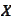 .
The solution
is
.
The solution
is
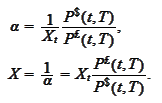
|
|
(Forward exchange rate)
|
|