e consider an economy with one deterministic asset
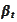 given by the
equation
given by the
equation
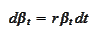 and one stochastic asset
and one stochastic asset
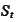 evolving according
to
evolving according
to
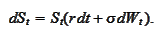 The
The
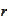 and
and
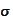 are some real numbers. The
are some real numbers. The
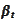 is the numeraire.
Indeed,
is the numeraire.
Indeed,
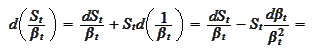
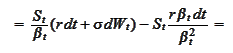 and the
and the
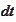 term cancels
out
term cancels
out
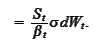 We select
We select
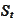 as a new numeraire. We
compute
as a new numeraire. We
compute
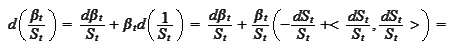
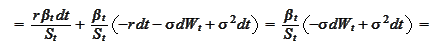
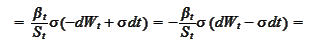
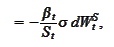 where
where
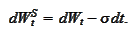 Hence, under the numeraire
Hence, under the numeraire
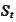 ,
the set of defining SDEs has the following
form
,
the set of defining SDEs has the following
form
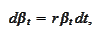
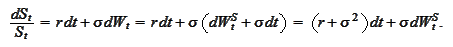
|