|
|
Construction of (G)MRA and wavelets on an interval.
|
|
o far all wavelet considerations were conducted on
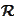 .
In this section we construct wavelets on an interval
.
In this section we construct wavelets on an interval
![$\left[ a,b\right] $](graphics/notesCF__1__5764.gif) while preserving approximation and orthogonality properties and construct
wavelets satisfying boundary conditions.
while preserving approximation and orthogonality properties and construct
wavelets satisfying boundary conditions.
|
|
|
|