e will use the proposition (
Toy
approximation in energy norm
) to approximate the difference
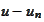 in
in
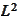 norm.
norm.
Let
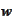 be the solution of the
problem
be the solution of the
problem
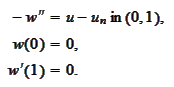 Let
Let
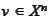 .
We
estimate
.
We
estimate
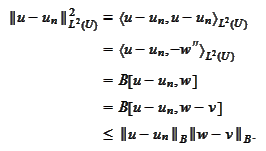 Thus
Thus
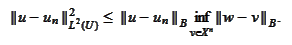 We assume that the following condition holds.
We assume that the following condition holds.
Under such assumption we
continue:
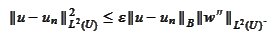 We recall
We recall
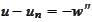 thus
thus
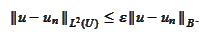 We use the proposition (
Toy
approximation in energy
norm
):
We use the proposition (
Toy
approximation in energy
norm
):
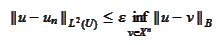 and apply the condition (
Energy
approximation
):
and apply the condition (
Energy
approximation
):
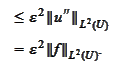
|